- Report Summary
- Methodology
- Request for ESG Consultation
Policies and strategies focused on improving environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investments are gaining traction globally for creating long-term business value. This involves companies, consumers, and governments who utilize ESG principles as a framework for increasing their assets and attracting thematic investments.
Third-party logistics, also known as 3PL, is the practice of outsourcing various logistics and supply chain management functions to a third-party provider. Development of transport logistics and related infrastructure in the Middle East and Asia regions, fast progress of the e-commerce market coupled with the development of new technologies, increasing working capital, and globalization that led to the demand for efficient inventory management services are some of the significant factors that drive the global third-party logistics market.
In a 3PL market, ESG factors have become increasingly important, encompassing challenges and opportunities for 3PL providers and their clients. While there is a growing emphasis on socially responsible initiatives such as achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), multi-dimensional ESG aspects, including business ethics, labor conditions, carbon emissions, human rights, renewable energy, anti-corruption, and product packaging, are key ESG areas that companies in this industry look to address. However, the logistics industry, which creates a multi-dimensional impact on various ESG aspects, lacks a standardized measurement framework to understand the impact of ESG within its current ESG measurement practice. This is mainly due to the non-standardized and unstructured business data with small-sized and medium-sized supply chain management and logistics firms.
Key ESG Trends in the Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Market:
The third-party logistics market is evolving in response to increasing awareness of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) issues in the market.
Environmental Trends:
In terms of the environment, the investment in the market is driven by awareness of companies on carbon emissions control, usage of recycled products, waste management policies, implementation of the 3R methodology, green sourcing, and low carbon travel. To address these challenges, key players in the third-party logistics market are crafting policies and strategies to promote green transportation, such as electric and hybrid vehicles, to counter carbon emissions. Fedex, one of the prominent providers in this market, has leveraged innovative technologies to transition to a fossil fuel-free fleet, enabling pick-up, delivery, and last-mile delivery. Some other firms have developed innovative solutions in their logistics, including eliminating cardboard and single-use plastic and replacing secondary packaging with recycled materials and secondary raw materials. Simple solutions such as replacing polyethylene firms with plastic bubble wraps and reducing the thickness of packaging have also reduced packaging volume and optimized logistics.
Some key players in the market have created sustainable warehouses and facilities that are energy-efficient. The same company has facilities that areLeadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) certified in the U.S. and Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method (BREEAM) in Europe, indicating the efforts to conserve energy. In addition, key players of the third-party logistics market are also initiating and executing strategies that make packaging more eco-friendly and reduce packaging waste. For instance, a 3PL company based out of Germany has a packaging solution named BigBelt. The packaging cover can be used more than 500 times, which helps reduce packaging waste.
Social Trends:
Certain research indicates social criteria to have relative importance on supply chain logistics over the other two aspects of the ESG. Dimensions or KPIs within this aspect focus on supply chain transparency, fair labor practice, work-life balance, diversity and inclusion, human rights within the supply chain, and workforce health and safety. On the one hand, leading firms in the third-party logistics market have employed technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Blockchain to ensure transparency in the supply chain. For instance, a Germany-based 3PL company has incorporated smart solutions such as IoT, including sensor technologies that increase visibility, quality, and security and help in regulatory compliance. Certain other firms in this market have partnered with blockchain technology firms to create sustainable supply chain management and blockchain-as-a-service for supply chain managers, creating a more sustainable and transparent supply chain management.
On the other hand, certain KPIs, including human rights and fair labor practice, garner increasing attention from consumers and suppliers. A key player in the market, Kuehne + Nagel has a Human Rights, Diversity, and Equal Opportunities statement and a social governance policy that makes inclusion and diversity a top priority at the firm. However, the company was embroiled in a recent controversy where it opposed providing decent pay to some workers in its Ontario facility in Canada.
Governance Trends:
While the governance facet is identified to have a relatively moderate impact on the sustainability of the 3PL logistics market compared to the environmental and social aspects, it is undoubtedly indispensable due to the importance of meeting regulatory requirements. Governance performance is the key to improving corporate reputation, supplier/customer relationships, risk management, and cybersecurity practices. The non-standardized business data with small and medium-sized third-party logistics firms means regular audit of financial statements, monitoring of supplier satisfaction, development of data confidentiality policies, risk management, privacy policies, and ESG metrics compensation goals hold significance within governance parameters for these firms. Global integrated logistics firm Alps Logistics Co., Ltd, operating in Japan, has established a Sustainability Promotion Committee to liaise with business operating units and report to the board of directors, thereby strengthening sustainable business practices and also has a diverse and inclusive board that includes more than 50% independent directors.
Macro-economic trends in the Third-Party Logistics Market:
Third-Party Logistics market at a global scale has generated revenue of USD 1,034.43 billion in 2022 and is forecast to expand with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.7% from 2023 to 2030. Companies operating in the 3PL market have constantly evolving strategies to meet ESG goals and have incorporated environmentally and socially sustainable policies and practices to improve sustainability and attract potential investments. From an environmental perspective, regulatory measures are expanding globally to curb emissions by tightening emissions standards in the European Union. Also, countries in the EU have established targets and policies to prevent air pollution and have legislation to regulate sustainable freight transport. Similar binding regulations are required in fast-developing countries to promote ESG across the 3PL market globally. In India, in 2023, the state government of Kerala is working on a ‘first of its kind’ draft ESG policy that aims to incentivize industries compliant with ESG activities, including the logistics industry, to promote ESG investments in the state.
Key Companies operating in the third-party logistics market:
• BDP International
• Burris Logistics
• C.H. Robinson Worldwide, Inc.,
• CEVA Logistics
• DSV
• DB Schenker Logistics
• FedEx
• J.B. Hunt Transport, Inc.,
• Kuehne + Nagel
• Nippon Express
• United Parcel Service of America, Inc.
• XPO Logistics, Inc.
• Yusen Logistics Co. Ltd.,
Scope of the Third-Party Logistics Market ESG Thematic Report:
• Macro-economic and ESG-variable analysis of the industry, including regulatory, policy, and innovation landscape
• Key insights on infrastructure developments and ESG issues affecting the theme
• Identify key initiatives and challenges within the industry
• Identify ESG leaders within the industry
• Understand key initiatives and the impact of companies within the sector to fuel an informed decision-making process.
• Analysis of industry activities based on multi-media sources, including significant controversies and market sentiment
Key aspects of the report:
• Offers a global perspective of the third-party logistics market and the policies and measures taken by players to overcome the challenges faced in terms of • Environment, Social, and Governance.
• Key insights into the sustainability practices of major players in the market, including peer insights and company ESG performance reports.
• Innovations, green deals, and patents of firms operating in the market.
• ESG scores and industry benchmarking of the policies, practices, and performance of the key players in the industry.
Research methodology
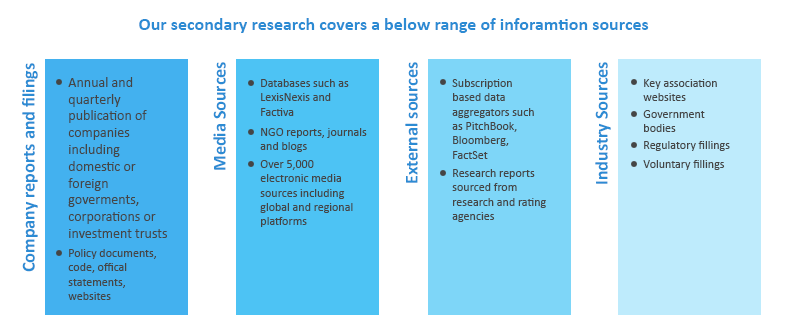
Grand View Research (GVR) employs a holistic and robust research methodology focused on delivering precision. Our ESG key issues are selected following a thorough materiality analysis run by our taxonomy committee. We examine leading business journals relevant to the industry sector and where applicable references are made to a range of sources including regulatory agencies, trade associations, company filings, white papers, and analyst reports during the due diligence on data aggregation. In addition, a recurring theme that remains central to all our research reports remains data triangulation which aims to dive into the market from thematic context, regulation, and industry benchmarking, including SWOT analysis.
Eligibility Criteria and Company Selection
Each public company is curated by our senior researchers following a comprehensive study of their business involvement around a specific theme. The involvement extends to subsidiaries based on at least 50% holding by the parent company. Following this, we analyze fundamental financial indicators, including revenue and market capitalization to ensure a diverse set of companies that fairly represent the sector are included. Additionally, GVR researchers ensure the disclosure level of each company across the material ESG key issues.
Scoring Methodology
Each ESG metric is assigned a specific weight based on its relevance across sectors. Below are the aggregated weights across pillars, which are derived from each metric.
| Environment | Social | Governance |
| 40% | 30% | 30% |
GVR’s proprietary ESG score is calculated using a weighted average method at:
• Key issues level
• Pillar level
• Company level and,
• Theme level
Data Mining
Data is obtained and collated from diverse source points. The data collected is continuously cleansed to ensure that only validated and verifiable sources are analyzed. In addition, data is also mined from a large number of in-house syndicated research reports inventory as well as through paid databases and premium content. During this research report, we conducted multiple primary interviews across the globe supported by our Primary Research Panels through the delivery of a mix of paid and unpaid interviews. We also send and receive responses from a wide section of industry participants through a carefully crafted and comprehensive survey questionnaire. We triangulate these data into quant models and generate qualitative insights. Evolving industry dynamics that shape drivers, restraints, and pricing are also gathered. As a result, the published content includes proprietary data and meaningful insights.
Fundamental ESG data:
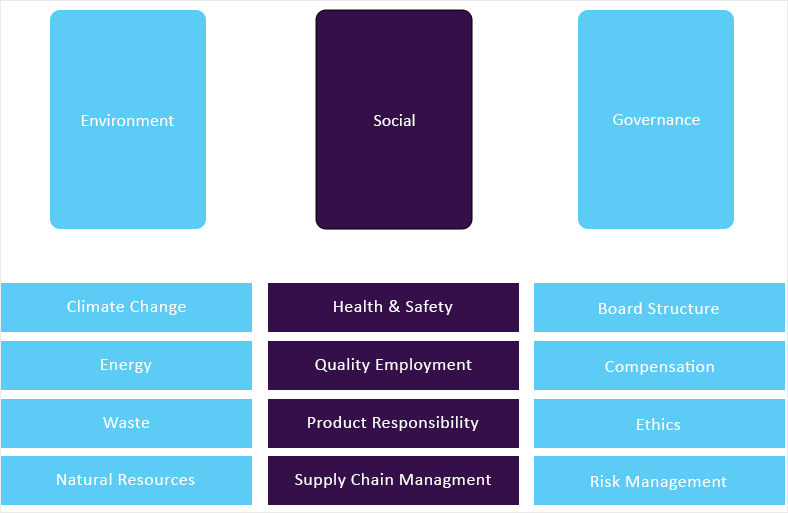
GVR’s ESG taxonomy committee maintains the framework and ensures it is updated quarterly considering market updates and relevance. Framework includes 65+ fundamental ESG metrics that are identified following a thorough materiality assessment. Below is GVR’s ESG Level-I framework:
Alternative ESG data:
GVR also analyzes macro-economic factors that impact or drive the growth of respective sectors. This includes
• Deep dive analysis of policy and regulatory landscape that has potential towards shaping the future of businesses
• Innovation quotient of a sector to gauge prospective evolution of a theme and related opportunities
• Investment scenario, including mergers & acquisition, funding and other deals to assess the investment appetite for a particular theme
• Other market activities, including market size, growth forecasts among others.
Information sources