ESG metrics, also known as Environmental, Social, and Governance metrics, are a set of criteria and key performance indicators that investors, companies, and stakeholders use to evaluate and measure a company’s performance in the areas of sustainability, responsible business practices, and ethical governance. These metrics provide a framework for assessing a company’s impact on society and the environment, as well as its overall business practices. While the environmental metrics focus on a company’s impact on the natural world in terms of the performance on indicators that influence climate change such as energy consumption and Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions, the social metrics focus on assessing the company’s relationships with its employees, customers, suppliers, communities, and other stakeholders. On the other hand, governance metrics consider the internal policies, procedures, and leadership structures of a company for analysis which is of significance to the investors and regulatory bodies. The governance framework often includes indicators like board diversity, executive compensation, anti-corruption policies, shareholder rights, and adherence to legal and regulatory standards.
ESG metrics are used by various stakeholders, including investors, rating agencies, and socially responsible organizations, to make informed decisions about investing, lending, partnering with, or supporting companies. Companies which perform well in ESG metrics are often seen as more attractive to investors and may have access to a broader range of financing options. They also tend to build stronger relationships with customers and employees who prioritize ethical and sustainable practices.
Significance of ESG Metrics in ESG Reporting and Disclosure
ESG reporting and disclosure have become increasingly important in recent years as companies recognize the significance of sustainable and responsible business practices in a global context. Organizations of all sizes acknowledge the advantage and necessity to be more transparent about their ESG practices. Many stock exchanges, regulators, and industry associations such as the U.S. Securities Exchange Commission (SEC) or the Bahrain Bourse Stock Exchange require or encourage companies to report on their ESG performance, and ESG data is often integrated into financial reporting and analysis to provide a more comprehensive view of a company’s overall health and impact on society and the environment.
ESG metrics play a key role in developing ESG disclosures that provide stakeholders, including investors, regulators, customers, and the public, with critical information on a company’s commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices. These metrics enable transparent and standardized reporting, fostering trust and accountability in the corporate world. Moreover, ESG metrics promote corporate responsibility and help businesses adapt to a changing global landscape, where sustainability is not just a moral imperative but a strategic imperative for long-term success. In essence, ESG metrics serve as the foundation for meaningful ESG disclosures, guiding companies in their journey towards a more sustainable and equitable future.
ESG metrics have a wide range of applications in the business world and beyond. Even though metrics of this kind will have similarities in terms of the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) across the varied set of stakeholders, each stakeholder utilizes different scoring techniques based on their problem statement to reach a relevant and holistic decision about the importance of an ESG metric. The following table provides insights about the relevance of ESG metrics for each stakeholder:
| S. No | Stakeholder | Subject Matter | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Investors | ESG Risk Mitigation, Sustainable Portfolio Performance, Sustainable investment | ESG metrics help investors assess and manage risks related to their investment portfolio and to ensure that their investments align with their set of values and principles. |
| 2 | Customers | Product Sustainability, Environmentally-conscious Decision-making | ESG metrics, maintained formally or informally, allow customers to make informed choices that align with their values as with changing times consumers prefer to support businesses that prioritize sustainability, social responsibility, and ethical governance. |
| 3 | Employees | Workplace Retention, Job Satisfaction, Diversity, Equality, and Inclusion (DEI) | Companies which include ESG considerations tend to offer better working conditions, diversity and inclusion, and a sense of purpose, making them attractive to talent. |
| 4 | Regulatory Bodies | ESG Compliance and Reporting | Governments may require companies to report on specific ESG factors, and the metrics help ensure this reporting is accurate and transparent. |
| 5 | Business Competitors | ESG Benchmarking, Sustainable Businesses | Companies use ESG metrics to benchmark their own performance against industry peers. This competitive analysis can drive continuous improvement and innovation in ESG practices. |
| 6 | Financial Institutions | ESG Risk Assessment, Sustainable Investment, Ethical Investment, | ESG metrics can influence lending and credit decisions, as they help assess the risk associated with a borrower’s sustainability practices. |
Devising effective ESG Metrics:
ESG metrics is built by varied industries and sectors with different set of goals but in today’s business world almost every stakeholder requires a regular review and update of their operations to adapt to changing non-monetary circumstances and emerging issues. This is where having extensive ESG metrics integrates with the broader and global idea of ESG. Even though ESG holds a vast horizon worldwide, development of ESG metrics involves some activities which are widely applicable to all kinds of stakeholders along with some actions which differentiate from sector to sector.
It is essential for all the sectors to understand their unique business context, objectives, and stakeholder expectations before setting up an ESG metrics. To set the business context it is imperative for the stakeholders to build a process of identifying most material ESG issues which involves thorough
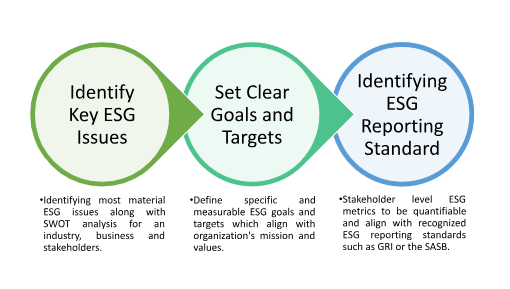
Fig 01: Steps for devising an ESG Metrics
asessment of risks, opportunities and the issues which matter the most to the set of investors and creditors and regulatory bodies specific to their field of operations. These issues must also align with the broader missions and values of the organization. For instance, metrics critical to the real estate sector include energy efficiency, carbon emissions, employee turnover, and occupancy rate among others. However, in terms of the Information Technology sector, the same may not be material. Similarly, the oil & gas industry might be more concerned with reporting emissions or health and safety of workers and focus on establishing protocols for governance indicators like bribery.
After the context is built, the process of developing an ESG metrics demands a set of measurable and time-bound goals which in addition can also concretize the mission and values of an institution or an organization. ESG goals gain their meaning in terms of global efforts with their alignment with global frameworks such as Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) which presents a link between an organization’s ESG practices and global ESG ecosystem and is an undeniable relevance building activity. Establishment of data collection processes and systems to track the chosen metrics and publishing this ESG data and metrics in an accessible, standardized, and transparent manner through an ESG report or disclosure completes the mechanism of ESG reporting along with ESG integration in the background. Hence, devising a relevant and unique ESG metrics is now an inevitable procedure which is suggested to almost all the industry-wide players.
The Importance of ESG Metrics in ESG Integration
ESG Metrics also finds its importance as a compass guiding company or an institution towards responsible and sustainable practices in ESG integration. This means by systematically measuring and monitoring ESG metrics, businesses can identify areas where they can improve their environmental impact, enhance social well-being, and strengthen corporate governance. ESG integration over well thought out metrics not only aligns a company’s values with societal expectations but also mitigates risks and identifies opportunities for innovation as it provides a structured framework for decision-making.
