Compliance, ESG Challenges & Framework, ESG Trends
- Report Summary
- Methodology
- Request for ESG Consultation
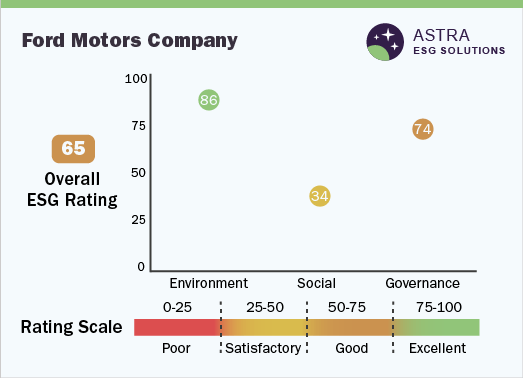
Environment, Social and Governance (ESG) at Ford Motors Company
The policies that impact environment, social, and governance, which are made by the companies, involving the consumers and the governments, are shaping the current trend in investments in an unprecedented manner.
Being one of the key leaders of the automotive industry, Ford Motor Company has focused on Environment, Social, and Governance, focusing on promoting an eco-friendly way of logistics, sustainable transportation, and community inclusive method of operations. In regard to this, Ford Motor Company has made policies that define its core ethical values of governance, striving to make a positive impact in all three areas of ESG and aims to closely align with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs) for promoting ESG performance and ESG impact.
Depletion of natural resources as well as the advancement of technology in the automotive industry, has led Ford Motor Company to adopt sustainable technologies and policies.
ESG Trends
The internal governance policies of the Ford Motor Company are aligned with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals and the company has aimed to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. At the core, the Ford Motor Company has sustainable policies inclusive of human rights policies, data protection policies, product safety and business ethics, and sound corporate governance policies.
To enable this goal, Ford Motor Company has made changes in its production operations to reduce climate change, where it has set a goal of making all of its products with net zero emissions by 2035. It aims to achieve this by introducing a new line of EV product range by 2035, both in passenger and commercial segments. The methods used to reduce the scope 1, scope 2, and scope 3 emissions are aligned with science-based targets and the company has made an Environmental policy to achieve the aforementioned targets. Further, the company has focused on the decarbonization of the supply chain to achieve net zero targets.
Introduction and execution of responsible material sourcing policy, which mandates the members of the supply chain to understand and responsibly mine minerals such as tin, tungsten, tantalum, and gold responsibly is a major environmental initiative by the company. Since the mining of metals causes heavy distress on the environment, Ford Motor Company’s focus on this issue steers a positive impact on the environment.
Furthermore, the usage of blockchain technology for tracking and investigating the cobalt sourcing for producing the EV production line the Ford is enabling the purchaser to track the data regarding the materials, promoting responsible mineral sourcing.
In regard to the social and governance aspects, Ford Motor Company drives a positive impact where it focuses on the promotion and integration of human rights, ensuring executive compensation is tied to non-financial metrics, increasing independent directors on board, and having a strong compliance culture.
Future of ESG at Ford Motors Company
Ford Motor Company’s revenue was around USD 127 billion. Ford Motor Company has made initiatives and policies that create a positive impact on the environment and society in parallel and these policies reflect the core values of the company, which aim at reducing the carbon footprint and emissions as well as promoting sustainability in terms of environment and human rights.
Research methodology
Grand View Research (GVR) employs a holistic and robust research methodology focused on delivering precision. Our ESG key issues are selected following a thorough materiality analysis run by our taxonomy committee. We examine leading business journals relevant to the industry sector and where applicable references are made to a range of sources including regulatory agencies, trade associations, company filings, white papers, and analyst reports during the due diligence on data aggregation. In addition, a recurring theme that remains central to all our research reports remains data triangulation which aims to dive into the market from thematic context, regulation, and industry benchmarking, including SWOT analysis.
Eligibility Criteria and Company Selection
Each public company is curated by our senior researchers following a comprehensive study of their business involvement around a specific theme. The involvement extends to subsidiaries based on at least 50% holding by the parent company. Following this, we analyze fundamental financial indicators, including revenue and market capitalization to ensure a diverse set of companies that fairly represent the sector are included. Additionally, GVR researchers ensure the disclosure level of each company across the material ESG key issues.
Scoring Methodology
Each ESG metric is assigned a specific weight based on its relevance across sectors. Below are the aggregated weights across pillars, which are derived from each metric.
| Environment | Social | Governance |
| 40% | 30% | 30% |
GVR’s proprietary ESG score is calculated using a weighted average method at:
• Key issues level
• Pillar level
• Company level and,
• Theme level
Data Mining
Data is obtained and collated from diverse source points. The data collected is continuously cleansed to ensure that only validated and verifiable sources are analyzed. In addition, data is also mined from a large number of in-house syndicated research reports inventory as well as through paid databases and premium content. During this research report, we conducted multiple primary interviews across the globe supported by our Primary Research Panels through the delivery of a mix of paid and unpaid interviews. We also send and receive responses from a wide section of industry participants through a carefully crafted and comprehensive survey questionnaire. We triangulate these data into quant models and generate qualitative insights. Evolving industry dynamics that shape drivers, restraints, and pricing are also gathered. As a result, the published content includes proprietary data and meaningful insights.
Fundamental ESG data:
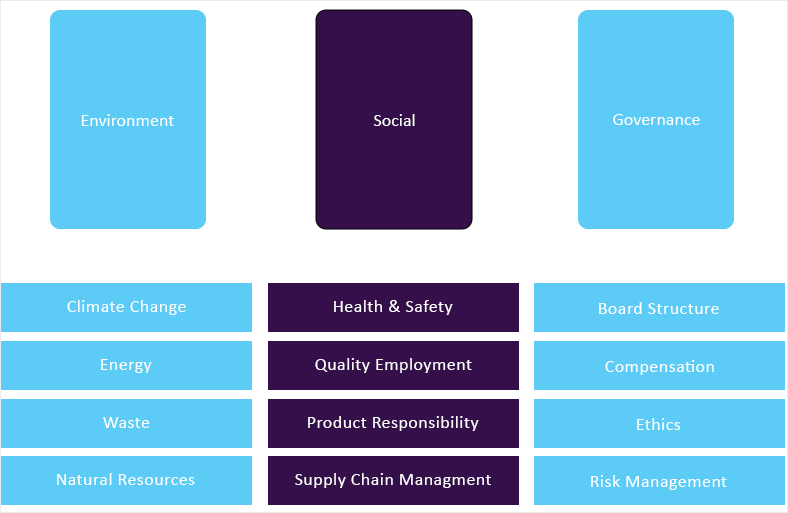
GVR’s ESG taxonomy committee maintains the framework and ensures it is updated quarterly considering market updates and relevance. Framework includes 65+ fundamental ESG metrics that are identified following a thorough materiality assessment. Below is GVR’s ESG Level-I framework:
Alternative ESG data:
GVR also analyzes macro-economic factors that impact or drive the growth of respective sectors. This includes
• Deep dive analysis of policy and regulatory landscape that has potential towards shaping the future of businesses
• Innovation quotient of a sector to gauge prospective evolution of a theme and related opportunities
• Investment scenario, including mergers & acquisition, funding and other deals to assess the investment appetite for a particular theme
• Other market activities, including market size, growth forecasts among others.
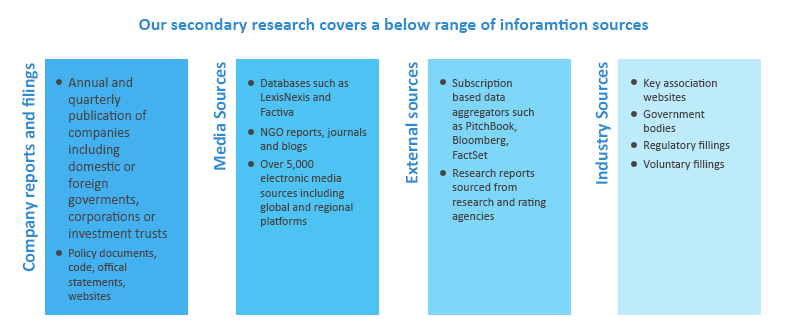
Information sources